Waste recycling refers to the process of collecting, sorting, and processing waste materials to convert them into reusable materials or products. It is a crucial component of waste management and a sustainable approach to dealing with waste.
The main objective of waste recycling is to reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills or incinerators and conserve natural resources by reusing materials. Recycling helps in minimizing environmental pollution, conserving energy, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting a circular economy.
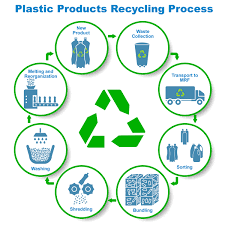
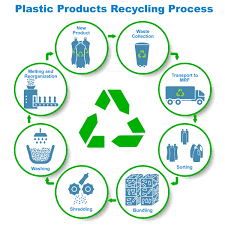
The process of waste recycling typically involves the following steps:
- Collection: Waste materials, such as paper, plastics, glass, metals, and organic waste, are collected from households, businesses, and industries. Collection methods may include curbside collection, drop-off centers, or specialized recycling facilities.
- Sorting and Separation: The collected waste is then sorted and separated based on material type. This process may involve manual sorting, automated sorting systems, or a combination of both. Separation ensures that different types of materials are handled and processed separately for effective recycling.
- Processing and Treatment: After sorting, the recyclable materials undergo various treatment processes to prepare them for reuse. This may involve shredding, crushing, melting, or cleaning the materials to remove contaminants and prepare them for the manufacturing of new products.
- Manufacturing: The processed recyclable materials are used as raw materials to manufacture new products. For example, recycled paper can be used to produce new paper products, recycled plastics can be transformed into new plastic items, and recycled metals can be used in various manufacturing industries.
- Distribution and Consumption: The recycled products are then distributed to markets and consumers for purchase and use. Consumers play a vital role in the recycling process by choosing products made from recycled materials, thereby creating demand and supporting the recycling industry.
Benefits of Waste Recycling:
- Resource Conservation: Recycling helps conserve natural resources by reducing the need for extracting raw materials from the environment. This includes saving energy, water, and other resources required for the manufacturing of new products.
- Waste Reduction: Recycling reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills or incinerators, which helps alleviate the strain on these disposal methods and reduces the associated environmental impacts, such as methane emissions and soil contamination.
- Energy Savings: Recycling often requires less energy compared to the production of new materials from virgin resources. For example, recycling aluminum requires significantly less energy than extracting and refining bauxite ore to produce new aluminum.
- Pollution Reduction: Recycling reduces the pollution associated with waste disposal. By diverting materials from landfills and incinerators, recycling helps mitigate air and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and the release of toxic substances.
- Economic Opportunities: Recycling industries create job opportunities, stimulate local economies, and contribute to the development of a circular economy. The recycling sector involves collection, sorting, processing, manufacturing, and distribution, creating a range of employment opportunities at various stages.
- Community Engagement: Recycling encourages community participation and environmental awareness. It promotes responsible waste management practices, encourages individuals to reduce, reuse, and recycle, and fosters a sense of environmental responsibility.
Overall, waste recycling plays a vital role in promoting sustainable waste management practices, conserving resources, reducing environmental impacts, and transitioning towards a more circular and sustainable economy.
What are 4 types of recyclable waste?
There are many different types of recyclable waste, but here are four common categories:
- Paper: This includes newspapers, magazines, cardboard, office paper, and other paper products. Recycling paper helps save trees and reduces the energy and water required to produce new paper.
- Plastic: Plastic is a versatile material found in various forms, including bottles, containers, packaging, and bags. Different types of plastic may have specific recycling requirements, so it’s important to check the recycling codes on the packaging to determine if they are recyclable.
- Glass: Glass containers, such as bottles and jars, can be recycled. Recycling glass saves energy and raw materials, and it helps reduce the amount of waste in landfills.
- Metal: Metals such as aluminum, steel, and tin are highly recyclable. Aluminum cans, food cans, metal packaging, and even scrap metal can be recycled. Recycling metals helps conserve natural resources and reduces greenhouse gas emissions associated with mining and manufacturing new metal products.
It’s important to note that the recyclability of certain materials may vary depending on the recycling facilities available in your area. Additionally, there are many other types of recyclable waste, including cardboard, textiles, electronics, and more. Proper sorting and disposal of recyclable waste can help contribute to a more sustainable environment.
What is the importance of recycling waste?
Recycling waste is of great importance for several reasons:
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Recycling helps conserve valuable natural resources such as trees, water, minerals, and fossil fuels. By reusing materials, we reduce the need for extracting and processing raw materials from the Earth. This helps to preserve natural habitats, prevent deforestation, and minimize the environmental impact of resource extraction.
- Energy Conservation: Recycling often requires less energy than producing new products from virgin materials. For example, recycling aluminum cans uses significantly less energy compared to mining and refining aluminum ore. Conserving energy reduces carbon emissions and helps combat climate change.
- Reduction of Landfill Waste: Recycling diverts waste from landfills, which are rapidly filling up around the world. By recycling, we can reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, minimizing the release of harmful substances and preventing soil and water pollution. This also helps to extend the lifespan of existing landfill sites.
- Reduction of Pollution: The production of goods from virgin materials often involves processes that generate pollutants, including greenhouse gases, toxic chemicals, and particulate matter. Recycling reduces the demand for new production, leading to lower pollution levels and improved air and water quality.
- Economic Benefits: Recycling can contribute to the economy by creating jobs in waste management, recycling facilities, and related industries. It can also save money for individuals, businesses, and governments by reducing waste disposal costs.
- Promoting Sustainability: Recycling is an essential component of a sustainable lifestyle. By practicing recycling and responsible waste management, we promote a circular economy where materials are reused, reducing the need for continuous extraction of finite resources. Recycling encourages a mindset of resourcefulness and reduces our overall impact on the environment.
It’s important to note that effective recycling requires proper sorting and clean materials. Education and awareness about recycling practices are crucial to ensure maximum benefits and minimize contamination.