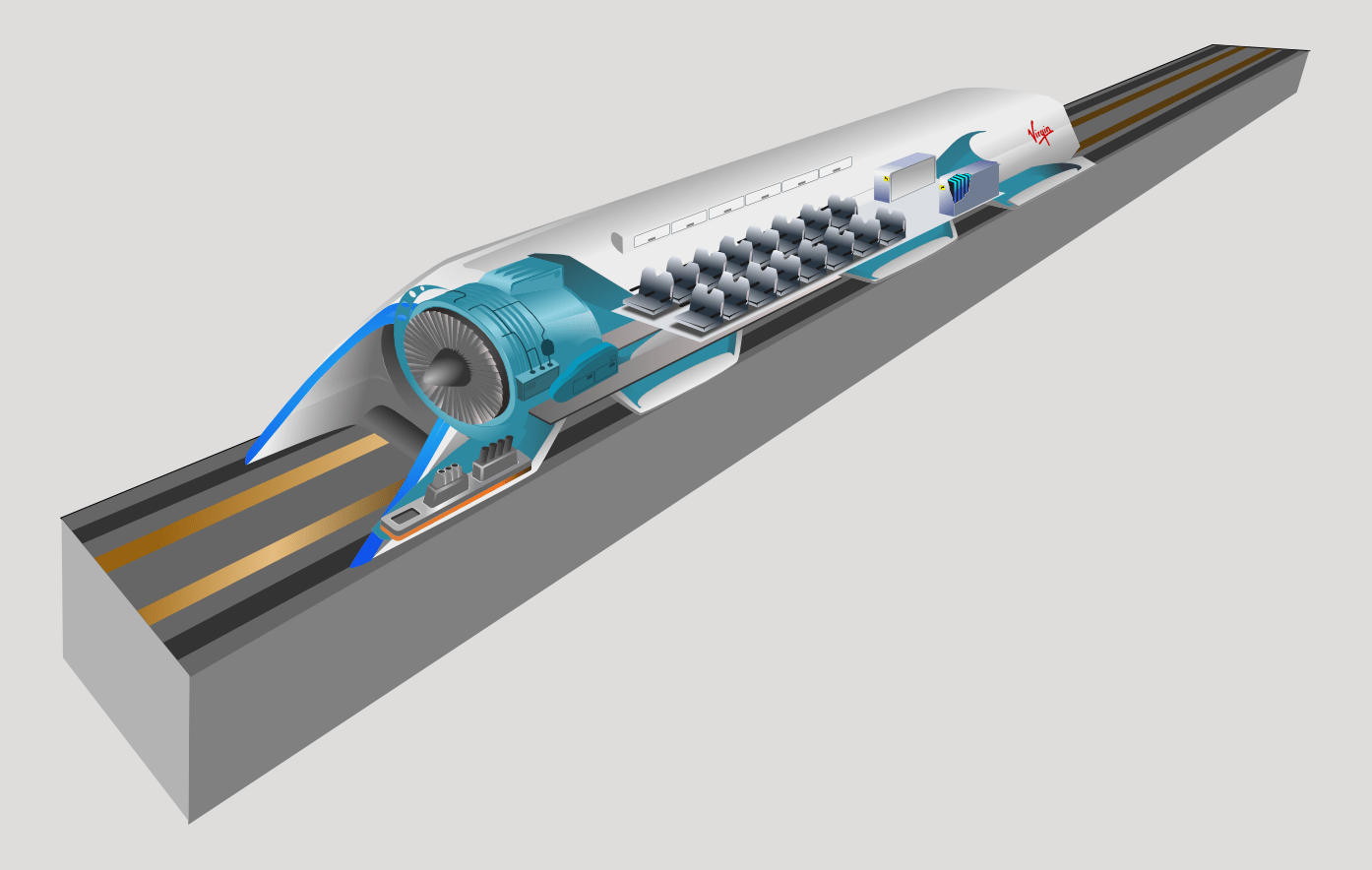
What is hyper loop ?
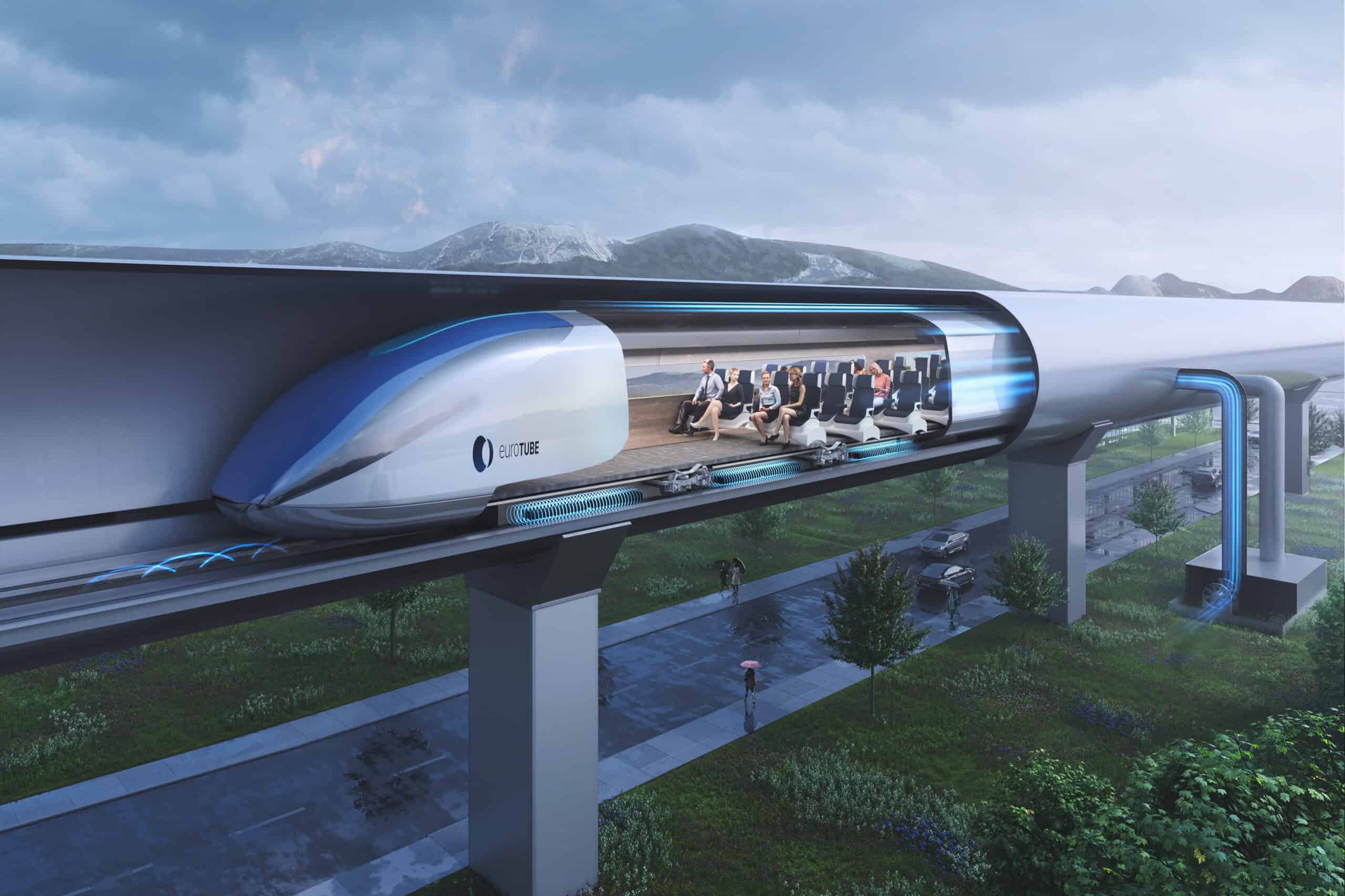
The Hyperloop is a proposed mode of transportation that envisions high-speed travel in a near-vacuum tube. It was initially conceptualized by Elon Musk, the CEO of SpaceX and Tesla, in 2013. The Hyperloop aims to provide a faster, more energy-efficient, and potentially more sustainable alternative to traditional modes of transportation like planes, trains, and automobiles.
The concept involves a low-pressure tube or system of tubes through which passenger pods or capsules would travel at very high speeds. The reduced air resistance in the near-vacuum environment would allow the pods to achieve speeds comparable to or greater than commercial airplanes, potentially exceeding 700 miles per hour (1,100 kilometers per hour).
The pods would be propelled using a combination of magnetic levitation (maglev) and linear induction motors. This technology would enable the pods to glide smoothly and efficiently through the tube, minimizing friction and energy loss. The system could be powered by renewable energy sources such as solar panels or wind turbines.
Several companies and organizations have taken up the challenge of developing the Hyperloop concept further. These include Virgin Hyperloop, founded by Richard Branson, as well as other startups and research teams. Prototype tracks have been built, and successful tests of the technology have been conducted, demonstrating the feasibility of high-speed travel in a vacuum environment.
The potential benefits of Hyperloop transportation include reduced travel times, decreased congestion on existing transportation infrastructure, lower energy consumption compared to airplanes, and the potential for sustainable transportation. However, there are still various technical, regulatory, and financial challenges to overcome before Hyperloop systems can be implemented on a large scale.
Why hyper loop is used ?
The Hyperloop concept is proposed as a potential mode of transportation for several reasons:
- High-speed travel: Hyperloop aims to provide extremely high speeds, potentially exceeding 700 miles per hour (1,100 kilometers per hour). This could significantly reduce travel times between cities, making it possible to cover long distances in a fraction of the time it takes with conventional modes of transportation.
- Energy efficiency: The near-vacuum environment inside the Hyperloop tube reduces air resistance, allowing the pods to travel with minimal energy consumption. Additionally, the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to generate the required electricity can make the system more environmentally friendly compared to modes like airplanes or cars.
- Reduced congestion: By providing an alternative mode of transportation, the Hyperloop could alleviate congestion on highways and airports, especially for popular travel routes. This can help reduce traffic jams, lower the demand for additional road or airport infrastructure, and provide more efficient transportation options.
- Sustainable transportation: The use of renewable energy sources to power the Hyperloop, coupled with its potential for energy efficiency, makes it a promising candidate for sustainable transportation. It could contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels in the long run.
- Potential cost-effectiveness: While the initial construction costs of a Hyperloop system could be significant, proponents argue that the operational costs could be relatively low compared to other modes of transportation. This could be due to the reduced energy consumption and minimal maintenance required for the tube infrastructure.
It’s important to note that while the Hyperloop concept holds promise, there are still several challenges to overcome before it becomes a widespread reality. These challenges include technical feasibility, regulatory frameworks, safety considerations, securing investments, and addressing potential social and economic impacts.
Where hyper loop is used ?
As of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021, there are no operational Hyperloop systems for passenger transportation. However, several companies and organizations are actively developing and testing Hyperloop technology. Here are a few notable projects:
- Virgin Hyperloop: Virgin Hyperloop, a company backed by Richard Branson’s Virgin Group, is one of the leading players in Hyperloop development. They have conducted successful test runs with their prototype system in Las Vegas, Nevada, showcasing the feasibility of the technology.
- The Boring Company: Founded by Elon Musk, The Boring Company has also been exploring the development of Hyperloop technology. While they initially focused on tunneling and underground transportation systems, they have expressed interest in integrating Hyperloop technology into their projects.
- Various international projects: Hyperloop development is not limited to a single country. Several countries have shown interest and are actively exploring the feasibility of Hyperloop systems. These include projects in places like the United Arab Emirates, India, and Europe.
It’s important to note that while there has been progress in the development and testing of Hyperloop technology, there are still significant challenges to overcome before it becomes a widely used mode of transportation. These challenges include regulatory approvals, safety considerations, infrastructure development, and securing the necessary investments. It may take several more years before Hyperloop systems are implemented on a large scale.
Case study on hyper loop
There were no operational Hyper loop systems for passenger transportation, which limits the availability of case studies. However, some key projects and initiatives that have made progress in Hyper loop development:
- Virgin Hyperloop One: Virgin Hyperloop, formerly known as Virgin Hyperloop One, has been actively involved in developing Hyperloop technology. They have conducted numerous successful tests, including a full-scale prototype test in 2017. Virgin Hyperloop has also partnered with governments and organizations worldwide to explore the implementation of Hyperloop systems, such as the proposed route between Pune and Mumbai in India.
- The Boring Company’s Hawthorne Test Tunnel: The Boring Company, led by Elon Musk, has been involved in developing tunneling technology as well as exploring the potential of Hyperloop systems. In 2018, they completed a test tunnel in Hawthorne, California, which serves as a platform for testing various transportation technologies, including Hyperloop pods.
- DP World Cargospeed: DP World, a global logistics company, partnered with Virgin Hyperloop to develop a cargo-focused Hyperloop system called DP World Cargospeed. The project aims to enhance the efficiency of cargo transportation, enabling faster and more sustainable delivery of goods across long distances.
- European Hyperloop Week: The European Hyperloop Week is an annual event that brings together student teams from universities worldwide to showcase their Hyperloop prototypes. It serves as a platform for innovation, collaboration, and knowledge sharing among the next generation of engineers and researchers in the field.
While these examples represent progress in Hyperloop technology, they do not constitute comprehensive case studies due to the lack of operational systems. However, ongoing developments and future advancements may provide more concrete case studies as Hyperloop technology matures and moves towards implementation.