Courtesy : .energy.gov
Green wind energy
Wind energy offers many advantages, which explains why it’s one of the fastest-growing energy sources in the world. To further expand ’s capabilities and community benefits, researchers are working to address technical and socio-economic challenges in support of a decarbonized electricity future.
Learn more about ongoing research to take advantage of these benefits and tackle wind energy challenges.
Advantages of Wind Power
- . There are over 120,000 people working in the U.S. wind industry across all 50 states, and that number continues to grow. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, wind turbine service technicians are the second fastest growing U.S. job of the decade. Offering career opportunities ranging from blade fabricator to asset manager, the wind industry has the potential to support hundreds of thousands of more jobs by 2050.
- Wind power is a domestic resource that enables U.S. economic growth. In 2021, wind turbines operating in all 50 states generated more than 9% of the net total of the country’s energy. That same year, investments in new wind projects added $20 billion to the U.S. economy.
- is a clean and renewable energy source. Wind turbines harness energy from the wind using mechanical power to spin a generator and create electricity. Not only is wind an abundant and inexhaustible resource, but it also provides electricity without burning any fuel or polluting the air. Wind continues to be the largest source of renewable power in the United States, which helps reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. Wind energy helps avoid 329 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions annually – equivalent to 71 million cars worth of emissions that along with other atmospheric emissions cause acid rain, smog, and greenhouse gases.
- Wind power benefits local communities. Wind projects deliver an estimated $1.9 billion in state and local tax payments and land-lease payments each year. Communities that develop wind energy can use the extra revenue to put towards school budgets, reduce the tax burden on homeowners, and address local infrastructure projects.
- Wind power is cost-effective. Land-based, utility-scale wind turbines provide one of the lowest-priced energy sources available today. Furthermore, wind energy’s cost competitiveness continues to improve with advances in the science and technology of wind energy.
- Wind turbines work in different settings. Wind energy generation fits well in agricultural and multi-use working landscapes. Wind energy is easily integrated in rural or remote areas, such as farms and ranches or coastal and island communities, where high-quality wind resources are often found.
Challenges of Wind Power
- Wind power must compete with other low-cost energy sources. When comparing the cost of energy associated with new power plants, wind and solar projects are now more economically competitive than gas, geothermal, coal, or nuclear facilities. However, wind projects may not be cost-competitive in some locations that are not windy enough. Next-generation technology, manufacturing improvements, and a better understanding of wind plant physics can help bring costs down even more.
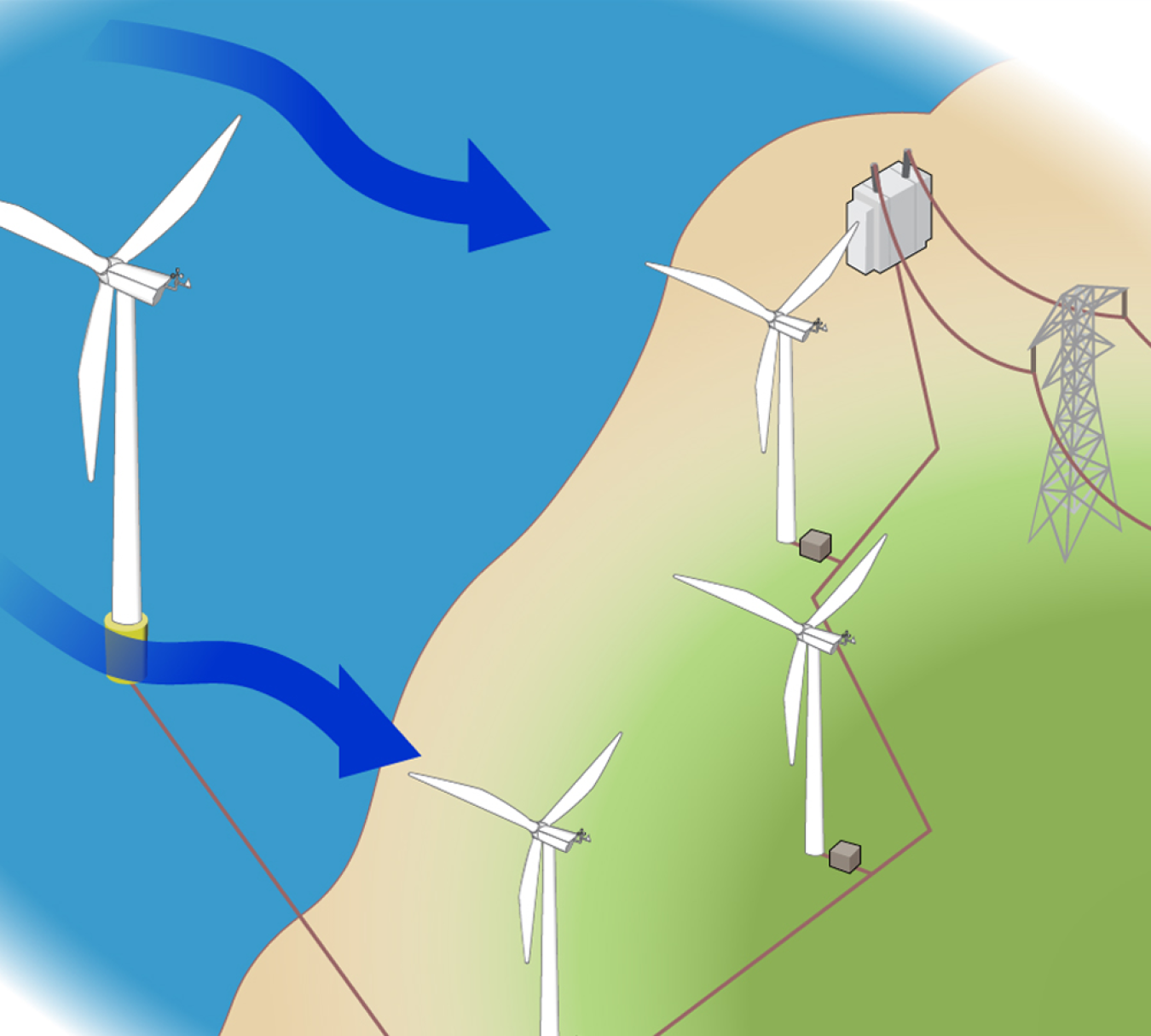
- Ideal wind sites are often in remote locations. Installation challenges must be overcome to bring electricity from wind farms to urban areas, where it is needed to meet demand. Upgrading the nation’s transmission network to connect areas with abundant wind resources to population centers could significantly reduce the costs of expanding land-based wind energy. In addition, offshore wind energy transmission and grid interconnection capabilities are improving.
- Turbines produce noise and alter visual aesthetics. Wind farms have different impacts on the environment compared to conventional power plants, but similar concerns exist over both the noise produced by the turbine blades and the visual impacts on the landscape.
- Wind plants can impact local wildlife. Although wind projects rank lower than other energy developments in terms of wildlife impacts, research is still needed to minimize wind-wildlife interactions. Advancements in technologies, properly siting wind plants, and ongoing environmental research are working to reduce the impact of wind turbines on wildlife.




