What is Green building ?
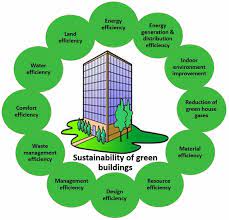
Green building, also known as sustainable or environmentally friendly building, refers to the design, construction, and operation of buildings that prioritize environmental responsibility, resource efficiency, and occupant well-being. Green buildings aim to minimize the negative impacts of the built environment on the environment and human health while maximizing energy efficiency, water conservation, and the use of sustainable materials.
Key features and principles of green building include:
- Energy Efficiency: Green buildings focus on reducing energy consumption through various strategies, such as efficient insulation, high-performance windows, energy-efficient lighting, advanced HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, and the use of renewable energy sources like solar or wind power.
- Water Conservation: Green buildings aim to minimize water usage through the installation of water-efficient fixtures and fittings, such as low-flow toilets and faucets, rainwater harvesting systems, and graywater recycling. Landscaping design also emphasizes native plants and efficient irrigation methods.
- Sustainable Materials: Green buildings promote the use of sustainable and environmentally friendly materials, such as recycled content, responsibly sourced timber, low volatile organic compound (VOC) paints and finishes, and non-toxic construction materials. This reduces the environmental impact associated with the extraction, production, and disposal of building materials.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Green buildings prioritize the health and well-being of occupants by ensuring good indoor air quality, sufficient natural daylighting, and effective thermal comfort. This involves proper ventilation systems, non-toxic materials, and the use of natural lighting strategies.
- Waste Reduction and Recycling: Green buildings implement waste management strategies, including the reduction of construction waste, recycling programs, and the use of recycled or recyclable materials. This minimizes the amount of waste sent to landfills and promotes a circular economy approach.
- Site and Location Selection: Green buildings consider the impact of site selection on the environment and community. Factors such as proximity to public transportation, access to amenities, and the preservation of natural habitats are taken into account.
- Life Cycle Assessment: Green building design considers the life cycle impact of a building, from construction to operation and eventual demolition. This involves evaluating the environmental impact of materials, energy consumption, and waste generation throughout the building’s life span.
- Certification and Standards: Various green building certification programs, such as GGBC (Global Green Building Council) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), provide guidelines and frameworks to assess and recognize sustainable building practices.
The benefits of green buildings include reduced energy and water costs, improved indoor air quality, enhanced occupant comfort and productivity, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and a positive contribution to overall environmental sustainability. Green building practices are increasingly being adopted worldwide as part of efforts to mitigate climate change, conserve resources, and create healthier and more sustainable built environments.
Green building design
Green building design encompasses a range of strategies and considerations to minimize the environmental impact of buildings while maximizing resource efficiency and occupant well-being. Here are some key aspects of green building design:
- Passive Design: Passive design strategies focus on utilizing natural elements and techniques to reduce the building’s energy needs. This includes optimizing building orientation for solar heat gain and daylighting, designing shading devices to control solar radiation, and incorporating natural ventilation to reduce reliance on mechanical cooling and heating.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient design principles aim to reduce the energy consumption of a building. This involves using high-performance insulation, energy-efficient windows and doors, efficient HVAC systems, LED lighting, and smart controls for energy management. Building envelope design, such as using reflective roofing materials, also plays a role in reducing heat gain.
- Water Efficiency: Green building design emphasizes water conservation by integrating water-efficient fixtures and systems. This includes installing low-flow toilets, faucets, and showerheads, as well as incorporating graywater systems for irrigation or toilet flushing. Rainwater harvesting systems can also be employed to collect and reuse rainwater.
- Sustainable Materials: The selection of sustainable materials is a crucial consideration in green building design. This involves using materials with low embodied energy, such as recycled content, rapidly renewable resources, and materials sourced from responsibly managed forests. Additionally, the use of non-toxic and low-VOC materials promotes indoor air quality.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Green building design prioritizes the health and comfort of occupants by optimizing indoor environmental quality. This includes proper ventilation systems, adequate daylighting, control of indoor pollutants, and the use of low-emission materials. Acoustic considerations are also important to create a comfortable indoor environment.
- Site Planning and Landscaping: Sustainable site planning involves considering the environmental impact of the building’s location and its relationship to the surrounding environment. Design elements may include preserving natural habitats, minimizing disturbance to the site, implementing stormwater management systems, and creating landscaping that requires minimal water usage.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Green building design often incorporates renewable energy systems to generate on-site clean energy. This can include solar photovoltaic panels, wind turbines, geothermal systems, or biomass energy systems. Integration of these renewable energy sources reduces the building’s reliance on fossil fuel-based energy.
- Life Cycle Assessment: Green building design considers the entire life cycle of a building, including the extraction of raw materials, construction, operation, maintenance, and eventual demolition. Life cycle assessment helps identify areas where environmental impacts can be minimized, and sustainable choices can be made throughout the building’s life span.
- Green Building Certifications: Green building design can be certified through recognized programs such as GGBC (Global Green Building Council) or BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method). These certifications provide a framework for evaluating and recognizing sustainable building practices.
Green building design requires a holistic and integrated approach, involving collaboration between architects, engineers, builders, and other stakeholders. By considering environmental sustainability, energy efficiency, water conservation, and occupant well-being from the design phase, green buildings can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient built environment.