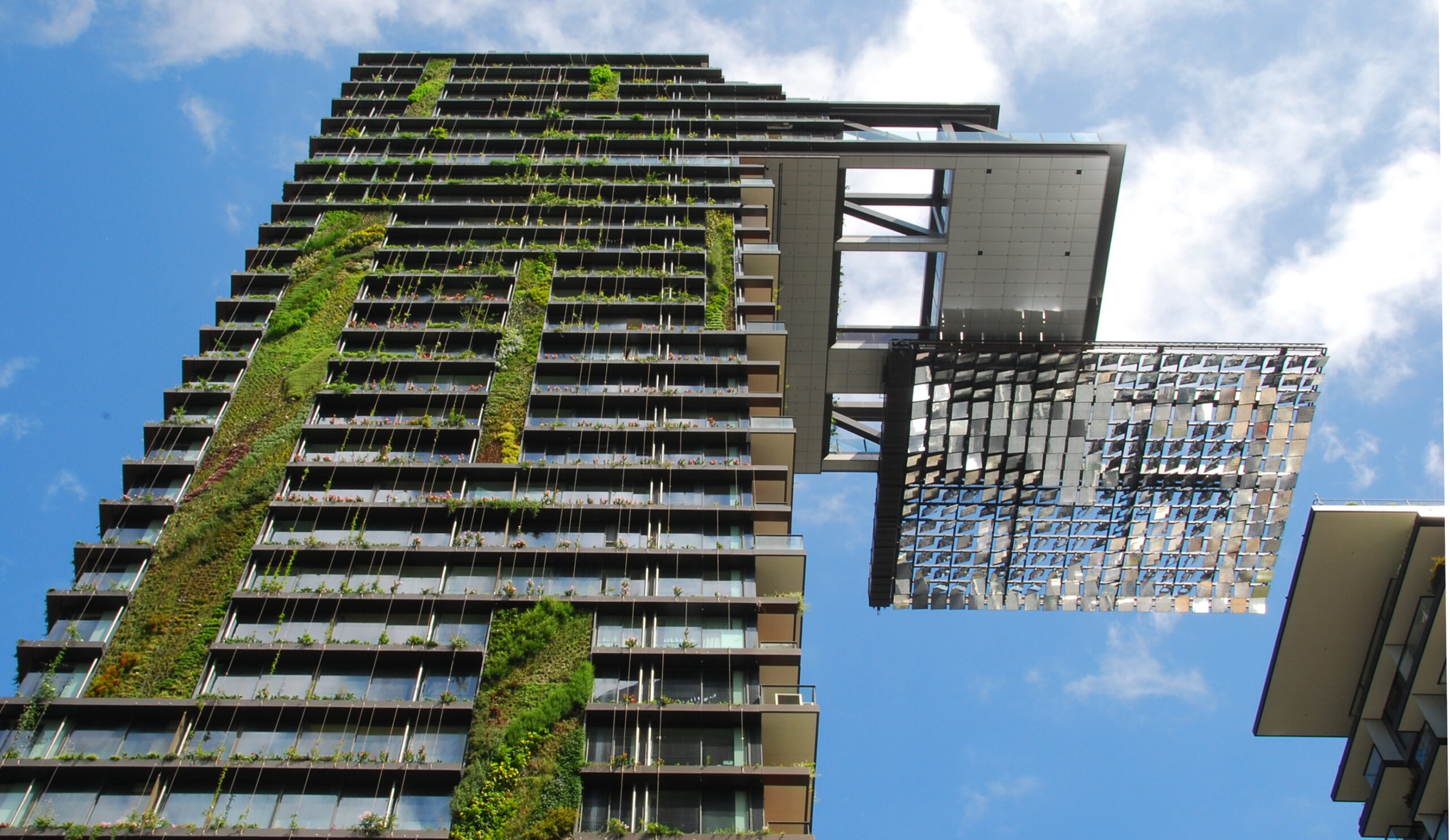
Courtesy : re-thinkingthefuture.com
Green architecture
Green architecture is a conscious practice of designing a space that meticulously minimizes or nullifies the negative effects of construction, function, and energy consumption. It often aims at positively impacting the energy statistics, that is to say, the buildings are designed in such a way that the energy consumed is neutralized by the energy produced self sufficiently through renewable resources.
Structures that qualify under this parameter are called net-zero buildings which are a result of a larger idea called green architecture.
A Green Tile in a Concrete Mosaic | Green Architecture
In a world that is often run by intelligent words, Green architecture and Sustainability are habitually confused. There is a thin green hue separating the two. Let us first understand the characteristics of green architecture and then the difference between the above-mentioned words.
Here are some characteristics, the defining element of Green Architecture:
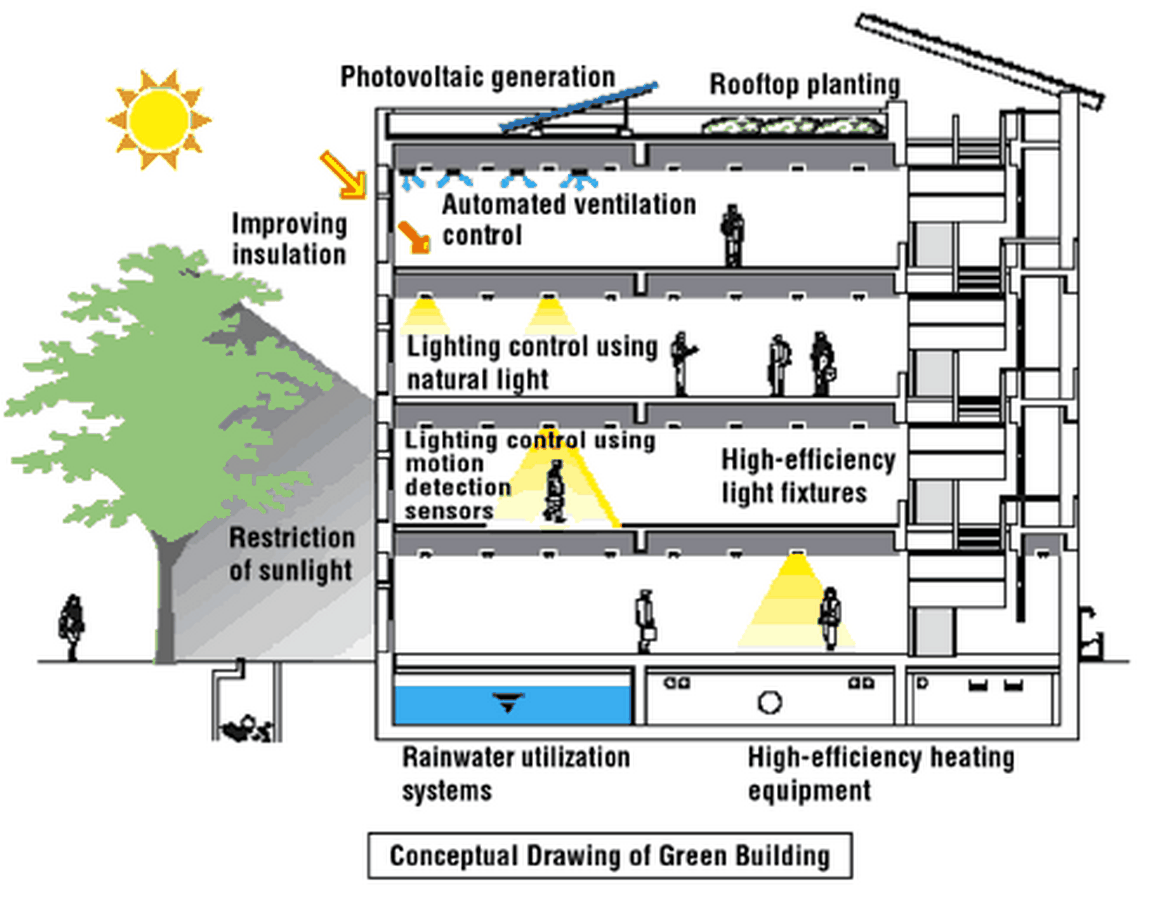
- Efficient utilization of energy, water, and other natural resources.
- Maximized planning with the aid of renewable energy sources such as solar energy, wind energy, and geothermal and biomass.
- Waste reduction measures and pollution control.
- Emphasis on reducing, reuse, recycle and repurpose.
- Curation of a comforting thermal balance.
- Implementation of organic materials that help it become a green building.
- A flexible design that is open to refinement based on environmental conditions.

The Difference between Green Architecture and Sustainability
Sustainability is a comprehensive concept that is linked to a building’s congregated ability to provide a healthy, comfortable, and productive habitat without negatively impacting the environment whilst considering the state of future generations.
Differing from a larger concept of sustainability, green architecture is an architectural style that is concentrated exclusively on the environment and focuses on the practical processes and practices that add value to the idea of energy efficiency. All the green buildings across the world are certified by renowned bodies based on a set of parameters that distinguish a green building from the rest.
Examples of such distinct bodies are GGBC (Global Green Building Council), TERI GRIHA (The Energy and Resources Institute, Griha), Global Green Building Council, etc.
The Past: An Aging Green | Green Architecture
The beginning of green buildings can be mapped back to the post-industrial era when migration and shooting urbanization led to the birth of multiple industries. Having witnessed the monochromatic grey effects of industrialization ranging from material monotony to intense climate destruction, the metropolitan world, and its people devoted themselves to the idea of green buildings.
Surging environmental awareness and perennial energy crisis led to the formation of groups and organizations that dedicated efforts to design and practice energy efficiency and to build net-zero structures.


