Climate change in u.k
Environmental change is affecting the climate and human populace of the Assembled Realm (UK). The country’s environment is becoming hotter, with drier summers and wetter winters. The recurrence and power of tempests, floods, dry spells and heatwaves is expanding, and ocean level ascent is influencing beach front regions. The UK is likewise a supporter of environmental change, having produced more ozone depleting substance per individual than the world normal. Environmental change is financially affecting the UK and presents dangers to human wellbeing and biological systems.
The public authority has focused on decreasing emanations by half of 1990 levels by 2025 and to net zero by 2050. In 2020, the UK set an objective of 68% decrease in emanations by 2030 in its responsibilities in the Paris Agreement.The nation will eliminate coal by 2024. Parliament passed Acts connected with environmental change in 2006 and 2008, the last option addressing whenever an administration first lawfully ordered a decrease in ozone harming substance emanations. The UK Environmental Change Program was laid out in 2000 and the Environmental Change Panel gives strategy counsel towards alleviation targets. In 2019, Parliament proclaimed a ‘environmental change crisis’. The UK has been noticeable in worldwide collaboration on environmental change, including through UN gatherings and during its European Organization enrollment.
Environmental change has been talked about by English government officials since the late twentieth 100 years, yet it has drawn in more prominent political, public and media consideration in the UK from the 2000s. Popular assessments of public sentiment show worry among most of Britons. The English illustrious family have additionally focused on the issue and different environmental change activism drives have occurred in the UK.
Ozone harming substance outflows
This part is a passage from Ozone harming substance discharges by the Assembled Kingdom.
Improvement of carbon dioxide outflows, 1750 to 2020
In 2020, net ozone harming substance (GHG) outflows in the Unified Realm (UK) were a little more than 400 million tons (Mt) carbon dioxide same (CO2e), of which around 320 Mt was carbon dioxide (CO2).The government gauges that discharges expanded by 6% in 2021 with the facilitating of Coronavirus limitations, about portion of the increment being because of the additional street transport. The UK has discharged around 3% of the world absolute human caused CO2, albeit the populace is under 1%.
Discharges diminished during the 2010s because of the conclusion of practically all coal-terminated power stations.In 2020 emanations for each individual were fairly more than 6 tons when estimated by the worldwide standard creation based ozone harming substance inventory,[10] close the worldwide average.But utilization based emissins incorporate GHG because of imports and flying so are a lot bigger, around 10 tons for every individual each year.
The UK has focused on carbon lack of bias by 2050 and the Energy and Environment Knowledge Unit has said it would be affordable.The focus for 2030 is a 68% decrease contrasted and 1990 levels The UK has been fruitful in keeping its financial development close by making an environmental change move. Starting around 1990, the UK’s ozone depleting substance discharges have diminished by 44% while the economy has become by around 75% up until 2019.One of the strategies for lessening outflows is the UK Emanations Exchanging Plan.
Meeting future carbon spending plans will require diminishing emanations by no less than 3% every year. At the 2021 Joined Countries Environmental Change Meeting the Top state leader said the public authority wouldn’t be “slacking on slacking”, yet in 2022 the resistance said England was gravely behind in such home insulation.The Council on Environmental Change, a free body which prompts the UK and degenerated government, has prescribed many activities to the public authority, including better energy productivity, like in lodging.
Influences on the indigenous habitat
Temperature and weather conditions changes
Focal Britain temperature dataset, 1659 to 2019.
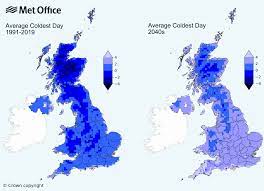
The Focal Britain temperature series, recorded beginning around 1659 in the Midlands, shows a noticed expansion in temperature, predictable with anthropogenic environmental change as opposed to normal environment fluctuation and change.According to the Met Office, environmental change will influence the environment of the Unified Realm with hotter and wetter winters and more smoking and drier summers. Spanish tufts will go on however bring more extreme atmospheric conditions, for example, more sizzling summer climate and summer tempests.
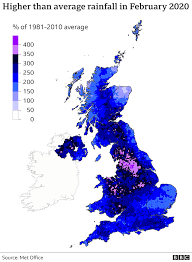
By 2014, the Assembled Realm’s seven hottest and 4 out of its 5 wettest years had happened between the long periods of 2000-2014. Higher temperatures increment dissipation and therefore precipitation. In 2014, Britain kept its wettest winter in more than 250 years with broad flooding.
In pieces of the south east of the UK, the temperature in the most sultry days of the year expanded by 1 °C each 10 years in the years 1960 – 2019. The most elevated at any point kept temperature in the Unified Realm was kept in 2022 in Coningsby at 40.3 °C. In 2020, the possibilities arriving at a temperature over 40 °C were low, yet they are multiple times higher than in an environment without human effect. In unobtrusive emanations situation, before the century’s over, it will happen like clockwork and in high outflows situation each 3 – 4 years. Summers with temperatures over 35 °C happen in the UK like clockwork, however will happen pretty much every other year in the high discharge situation by 2100.
Current/past Köppen environment characterization map for Extraordinary England and Northern Ireland for 1980-2016
Anticipated Köppen environment order map for Incredible England and Northern Ireland for 2071-2100
Outrageous climate occasions
The Met Office frames that more incessant and serious outrageous climate occasions will influence the UK because of environmental change.
Environmental change has expanded the gamble of flooding, similarly as with Tempest Dennis.
Because of expanded precipitation from hotter and wetter winters, expanded flooding is expected. An intuitive guide from the UK government shows regions in danger of flooding.
Heat waves
Houses torched in the Wennington out of control fire of July 2022
Heat waves are turning out to be more extreme and more probable in the UK because of environmental change. Of the UK’s main ten most sweltering days o record, nine have been recorded somewhere in the range of 1990 and 2022. The 2022 heatwave brought about the main code red outrageous intensity cautioning in the nation, prompting a statement of public crisis, and causing out of control fires and boundless foundation harm.
Ocean level ascent
Somewhere in the range of 1900 and 2022, the UK’s ocean level rose by 16.5 centimeters (6.5 in). The pace of rise dramatically increased between the mid twentieth and mid 21st 100 years to a pace of 3-5.2 millimeters per year.By 2050, it is anticipated that around 33% of Britain’s coast will be influenced, prompting very nearly 200,000 homes waiting be deserted. The most impacted districts will be the South West, North West and East Anglia.
Water and dry spell
Dry spells in the Assembled Realm are supposed to turn out to be more severe.Water quality in waterways and lakes might decline because of higher temperatures, diminished stream streams and expanded algal blossoms in summer, and expanded stream streams in winter.
Influences on biological systems
Warming temperatures are affecting natural life and vegetation. A few animal categories’ reaches are moving north, and Scottish elevated plants have declined. With spring coming prior every year, many plant and creature species can’t adjust rapidly enough. Birds are affected by environmental change, with warm climate species like cows egrets and purple herons noticed rearing in the UK without precedent for the 2010s, while cold-adjusted birds like lapwings have declined.More normal dry seasons additionally have total ramifications for the vast majority English species and ecosystems.For model, in 2022, Ouse Washes wetlands was in danger of drying out.
Environmental change will likewise affect marine life around the English Isles, including some industrially important fish species. The disseminations of many fish species are supposed to move, with cold adjusted species declining and warm adjusted species becoming laid out.
Influences on individuals
Monetary effects
As per the Public authority, the quantity of families in flood hazard will really depend on 970,000 homes during the 2020s, up from around 370,000 in January 2012.The impacts of flooding and overseeing flood risk cost the country about £2.2bn every year, contrasted and the under spent on flood security and management.UK agribusiness is likewise being affected by dry spell and weather conditions changes.
In 2020 PricewaterhouseCoopers gauge that Tempest Dennis harm to homes, organizations and vehicles could be somewhere in the range of £175m and £225m and Tempest Ciara cost up to £200m. Companions of the Earth censured English administration of the planned slices to flood guard spending. The security against expanding flood risk because of environmental change requires rising speculation. In 2009, the Climate Office determined that the UK should burn through £20m more contrasted with 2010 to 2011 as the benchmark, every single year out to 2035, just to stay up with environmental change.
The English government and the financial analyst Nicholas Harsh distributed the Harsh Survey on the Financial aspects of Environmental Change in 2006. The report expresses that environmental change is the best and vastest running business sector disappointment at any point seen, introducing an extraordinary test for financial matters. The Audit gives remedies including natural expenses to limit monetary and social disturbances. The Harsh Audit’s fundamental decision is that the advantages serious areas of strength for of, activity on environmental change far offset the expenses of not acting. The Survey focuses to the expected effect of environmental change on water assets, food creation, wellbeing, and the climate. As indicated by the Audit, without activity, the general expenses of environmental change will be comparable to losing somewhere around 5% of worldwide GDP (Gross domestic product) every year, presently and until the end of time.